Leave Your Message
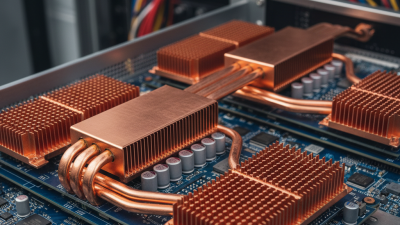
In modern industry, effective thermal management is crucial for performance and safety. Heat Transfer Pipes play a significant role in this process. These pipes are designed to move heat from one area to another, ensuring optimal temperatures are maintained. They are found in various applications, from electronics to heating systems. The functionality of Heat Transfer Pipes can be misunderstood. Some might think they only carry heat away. However, they also distribute heat evenly. This balance is vital for preventing overheating. When heat is not managed correctly, systems can fail or malfunction. This can lead to costly downtimes and repairs. Many engineers struggle to select the right type of Heat Transfer Pipe for their needs. The market offers multiple options, but not all are effective for every situation. Understanding specific requirements is essential. A poor choice can reduce efficiency and increase costs. Reflecting on these factors can lead to better thermal management solutions.
Heat transfer pipes play a crucial role in thermal management systems. They efficiently transport heat between components. This is essential in numerous applications from electronics to HVAC systems. A recent report by the International Energy Agency highlights that effective thermal management can improve energy efficiency by up to 30%. This efficiency leads to reduced energy costs and enhanced performance. Proper material selection for heat transfer pipes enhances their effectiveness. For instance, copper and aluminum are commonly used due to their thermal conductivity. However, the design must consider factors like pressure drops and flow rates. According to industry standards, an optimized design can lead to a 25% increase in heat transfer efficiency. Despite improvements, some systems still face challenges. Issues like corrosion and thermal fatigue can arise, leading to performance degradation. Regular maintenance and assessments are necessary to ensure longevity. Data suggest that poorly maintained systems can lose up to 40% of their efficiency over time. This highlights the importance of monitoring and updating thermal management strategies.
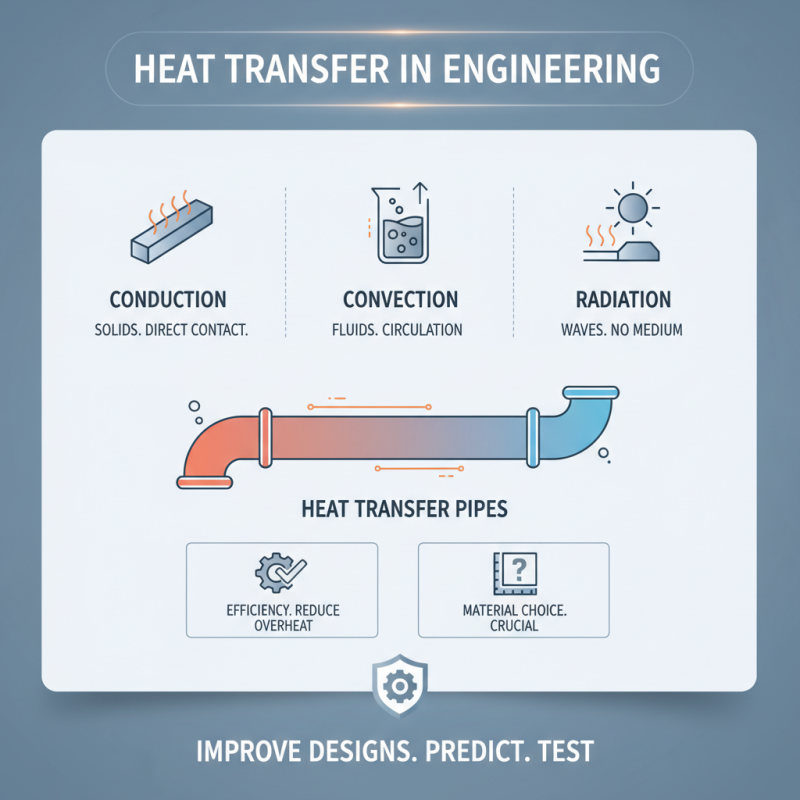
Heat transfer is a fundamental concept in engineering. Understanding how heat moves can enhance designs. Engineers often rely on three modes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Each mode plays a role in different systems. For instance, conduction occurs in solids, while convection happens in fluids. Engineers must grasp these principles to improve efficiency. In many applications, heat transfer pipes are vital. They carry thermal energy from one place to another. These pipes can reduce overheating, improving performance and lifespan. Yet, the material choice for these pipes can be tricky. Not every material conducts heat well. Sometimes, choosing the wrong one leads to increased energy loss. That's a common oversight in thermal management. Efficiency matters in all engineering fields. Poor heat transfer can lead to failure. It’s essential to test and simulate systems before implementation. Engineers can learn much from these steps. Reflections on past projects reveal areas for improvement. In thermal management, understanding heat transfer is just the beginning.
Heat transfer pipes are vital for effective thermal management in various industries. These pipes facilitate the transfer of heat from one medium to another, ensuring systems operate optimally. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, improving heat transfer efficiency can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%.
There are several types of heat transfer pipes, each suited to specific applications. For example, copper pipes are commonly used in HVAC systems due to their excellent thermal conductivity. Aluminum pipes, on the other hand, are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them popular in automotive applications. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of these materials can decline over time, and their thermal properties may not always meet the demands of advanced technologies.
Some emerging options include composite and nanofluid-enhanced pipes that promise improved performance. A 2022 study indicated that nanofluids can enhance heat transfer rates by 50% compared to traditional fluids. However, the implementation of these newer technologies may present challenges, such as higher costs and complexity in manufacturing. As industries evolve, finding the right balance between cost-efficiency and performance remains a significant hurdle.
| Type of Heat Transfer Pipe | Material | Application | Efficiency Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Pipe | Copper | HVAC systems | High |
| Aluminum Pipe | Aluminum | Automotive radiators | Moderate |
| Stainless Steel Pipe | Stainless Steel | Process piping | High |
| Plastic Pipe | PVC/CPVC | Drainage systems | Low |
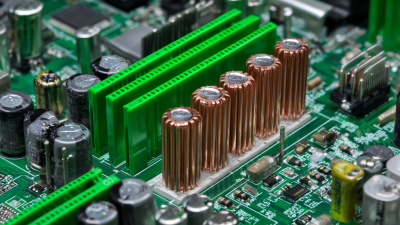
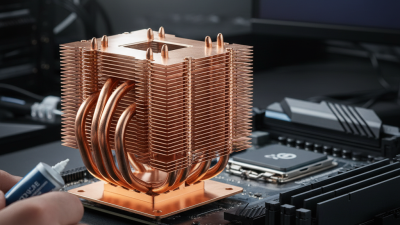
| Heat Pipe | Copper or Aluminum | Electronics cooling | Very High |
Heat transfer pipes play a crucial role in thermal management systems. These pipes facilitate the efficient transfer of heat, ensuring that devices operate within optimal temperature ranges. When heat builds up, it can lead to inefficiency or even failure of components. This is where heat transfer pipes excel, allowing excess heat to dissipate rapidly.
Using heat transfer pipes enhances energy efficiency significantly. For example, in industrial applications, these pipes can reduce energy consumption by maintaining consistent temperatures. This means less energy wasted on cooling or heating. A simple design often maximizes heat exchange, leading to better overall performance.
However, not all systems utilize heat transfer pipes effectively. Some designs overlook the placement of these essential components. This can result in uneven heat distribution and inefficiencies. It's vital to regularly evaluate how these pipes are integrated into systems. Optimizing their layout can lead to substantial improvements in energy usage. The potential benefits of heat transfer pipes should not be underestimated.
Heat transfer pipes play a crucial role in effective thermal management across various industries, including automotive and electronics. However, their implementation often comes with challenges. A recent report by the International Thermal Management Society indicates that approximately 30% of thermal management systems face inefficiencies due to improper pipe installation. This calls for better design practices and materials that enhance heat conduction.
One major challenge is the selection of materials. Not all materials perform equally under pressure and temperature fluctuations. A study by the Global Energy Efficiency Network reveals that using high-conductivity materials can boost efficiency by up to 20%. Yet, many companies opt for cheaper alternatives, risking system failure and increased energy consumption. This trade-off often leads to higher long-term costs, emphasizing the need for careful material consideration.
Another issue is maintenance. Heat transfer pipes require regular inspection to prevent leaks and blockages. Statistical data shows that nearly 25% of systems underperform due to maintenance neglect. Without addressing these challenges, the overall effectiveness of thermal management systems remains compromised. Improved training and awareness can mitigate these problems, driving the industry towards enhanced thermal efficiency.